| |||||||
| Anthem | "حماة الديار" (Arabic) Humat ad-Diyar | ||||||
| Capital | Damascus | ||||||
| Largest city | Aleppo | ||||||
| Other cities | Homs, ar-Raqqah, Daraa | ||||||
| Language | Arabic | ||||||
| Religion main |
Sunni Muslim, Shia Muslim, Alawite | ||||||
| others | Druze, Christianty | ||||||
| Ethnic Groups main |
Syrian Arabs | ||||||
| others | Turkmens, Circassians, Armenians, Kurds, Arameans, Greeks | ||||||
| Demonym | Syrian | ||||||
| Government | Unitary presidential semi-presidential republic | ||||||
| legislature | People's Council | ||||||
| President | Riad al-Asaad | ||||||
| Prime Minister | Riad Hijab | ||||||
| Area | 185,189 km² | ||||||
| Population | 20,994,000 (2020) | ||||||
| Established | 8 March 1920 | ||||||
| Independence | from France | ||||||
| declared | 14 May 1930 | ||||||
| recognized | 24 October 1945 | ||||||
| Currency | Syrian Pound (SYP) | ||||||
| Time Zone | EET (UTC +2) | ||||||
| summer | EEST (UTC +3) | ||||||
| Internet TLD | .sy, سوريا. | ||||||
| Calling Code | +963 | ||||||
| Organizations | United Nations Non-Aligned Movement | ||||||
Syria (Arabic: سوريا or سورية, Sūriyā or Sūrīyah), officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in Western Asia. De jure Syrian territory borders Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest, but the government's control now extends to approximately 30–40% of the de jure state area and less than 60% of the population.
History[]
Independent Syrian Republic[]
Upheaval dominated Syrian politics from independence through the late 1960s. In May 1948, Syrian forces invaded Palestine, together with other Arab states, and immediately attacked Jewish settlements. Their president Shukri al-Quwwatli instructed his troops in the front, “to destroy the Zionists". The Invasion purpose was prevention of the establishment of the State of Israel. Defeat in this war was one of several trigger factors for the March 1949 Syrian coup d'état by Col. Husni al-Za'im, described as the first military overthrow of the Arab World since the start of the Second World War.
In November 1956, as a direct result of the Suez Crisis, Syria signed a pact with the Soviet Union.
On 1 February 1958, Syrian President Shukri al-Quwatli and Egypt's Nasser announced the merging of Egypt and Syria, creating the United Arab Republic, and all Syrian political parties, as well as the communists therein, ceased overt activities. Syria seceded from the union with Egypt on 28 September 1961, after a coup.
Ba'athist Syria[]
The ensuing instability, following the 1961 coup culminated in the 8 March 1963 Ba'athist coup. The takeover was engineered by members of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party, led by Michel Aflaq and Salah al-Din al-Bitar. The new Syrian cabinet was dominated by Ba'ath members.
In the first part of 1967, a low-key state of war existed between Syria and Israel. Conflict over Israeli cultivation of land in the Demilitarized Zone led to 7 April prewar aerial clashes between Israel and Syria. After Israel launched a preemptive strike on Egypt to begin the Six-Day War, Syria joined the war and attacked against Israel as well. In the final days of the war, Israel turned its attention to Syria, capturing two-thirds of the Golan Heights in under 48 hours.
On 6 October 1973, Syria and Egypt initiated the Yom Kippur War against Israel. The Israel Defense Forces reversed the initial Syrian gains and pushed deeper into Syrian territory.
In early 1976, Syria entered Lebanon, beginning the thirty-year Syrian military occupation. Over the following 15 years of civil war, Syria fought for control over Lebanon, and attempted to stop Israel from taking over in southern Lebanon, through extensive use of proxy militias. Syria then remained in Lebanon until 2005.
Hafez al-Assad died on 10 June 2000. His son, Bashar al-Assad, was elected President in an election in which he ran unopposed.
Syrian Civil War[]
The Syrian Civil War was inspired by the Arab Spring revolutions. It began in 2011 as a chain of peaceful protests, followed by a crackdown by the Syrian Army. In July 2011, army defectors declared the formation of the Free Syrian Army and began forming fighting units. The opposition was dominated by Sunni Muslims, whereas the leading government figures were Alawites.
The civil war was resulted in peace talks between participants in Syrian Civil War -excluding ISIS- in Aleppo called Treaty of Aleppo. Syrian Kurdistan finally gained independence and then merged with Iraqi Kurdistan as Republic of Kurdistan. Syria holds an election in 2020, and surprisingly, leader of opposition, Riad al-Asaad won the election and became the new president of Syria.
Syrian Interim Government[]
Coming Soon
Geography[]
Syria is located in Southwestern Asia, north of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of mountain ranges in the west and inland a steppe area. In the east is the Syrian Desert and in the south is the Jabal al-Druze Range. The former is bisected by the Euphrates valley. A dam built in 1973 on the Euphrates created a reservoir named Lake Assad, the largest lake in Syria. The highest point in Syria is Mount Hermon (2,814 m; 9,232 ft) on the Lebanese border. Between the humid Mediterranean coast and the arid desert regions lies a semiarid steppe zone extending across three-quarters of the country, which receives hot, dry winds blowing across the desert. Syria is extensively run short, with 28 percent of the land arable, 4 percent dedicated to permanent crops, 46 percent utilized as meadows and pastures, and only 3 percent forest and woodland.
Politics and Government[]
Syria is formally a unitary republic. The constitution adopted in 2012 effectively transformed Syria into a semi-presidential republic, and later the new constitution adopted in 2020. The President is Head of State and the Prime Minister is Head of Government. The legislature, the Peoples Council, is the body responsible for passing laws, approving government appropriations and debating policy.

Riad al-Asaad, Current President of Syria.
The executive branch consists of the president, two vice presidents, the prime minister, and the Council of Ministers (cabinet). The constitution requires the president to be a Muslim but does not make Islam the state religion.
The constitution gives the president the right to appoint ministers, to declare war and state of emergency, to issue laws (which, except in the case of emergency, require ratification by the People's Council), to declare amnesty, to amend the constitution, and to appoint civil servants and military personnel. According to the 2012 and 2020 constitution, the president is elected by Syrian citizens in a direct election.
Syria's legislative branch is the unicameral People's Council. Under the previous constitution, Syria did not hold multi-party elections for the legislature, with two-thirds of the seats automatically allocated to the ruling coalition.

The parliament building in Damascus, Syria, as of 2016
Syria's judicial branches include the Supreme Constitutional Court, the High Judicial Council, the Court of Cassation, and the State Security Courts. Islamic jurisprudence is a main source of legislation and Syria's judicial system has elements of Ottoman, French, and Islamic laws.
Human Rights[]
The situation for human rights in Syria has long been a significant concern among independent organizations such as Human Rights Watch, who in 2010 referred to the country's record as "among the worst in the world." The US State Department funded Freedom House ranked Syria "Not Free" in its annual Freedom in the World survey.
But, after Riad al-Asaad is elected as president in 2020, and later he change Syria's constitution, he improved the human rights in Syria. Syria freed 90% of political prisoners. Syria is still using shari'a law and banned LGBT.
Military[]
The President of Syria is commander in chief of the Syrian armed forces, comprising some 500,000 troops upon mobilization. The military is a conscripted force; males serve in the military upon reaching the age of 18, but there are many women in the armed forces. Since the Syrian Civil War, the enlisted members of the Syrian military have dropped by over half from a pre-civil war figure of 325,000 to 150,000 soldiers in the army in December 2014, due to casualties, desertions and draft dodging, reaching between 178,000 and 220,000 soldiers in the army, in addition to 80,000 to 100,000 irregular forces.
Syria received significant financial aid from Arab states of the Persian Gulf as a result of its participation in the Persian Gulf War, with a sizable portion of these funds earmarked for military spending.
After the civil war, Syrian Armed Forces recruited 70,000 troops - 25,000 of them are recruited from Free Syrian Army - and built their military. Syria also started buy equipment from Western countries, like United States, Canada, UK, and Germany. Now, Syria ranked at 30th of most powerful military.
Foreign Relation[]
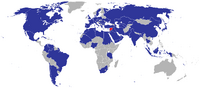
Diplomatic relation of Syria after the civil war.
Ensuring national security, increasing influence among its Arab neighbors, and securing the return of the Golan Heights, have been the primary goals of Syria's foreign policy. At many points in its history, Syria has seen virulent tension with its geographically cultural neighbors, such as Turkey, Israel, Iraq, and Lebanon. Syria enjoyed an improvement in relations with several of the states in its region in the 21st century, prior to the Arab Spring and the Syrian Civil War.
After the civil war, Syria improved their relations with some countries, such as Arab nations, Turkey, United States (Clinton's term, in 2020), United Kingdom, France, Pakistan, Brazil, Germany, India, Indonesia, and Nigeria. Syria also open more embassy in some countries. Syria later form an alliance with Palestine, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Lebanon, Iraq, and Egypt. Meanwhile, Syria's relationship with Russia and Iran also still good, but not with another former allies such as China, North Korea, and Cuba.
Syria now has some enemies, such as Israel and Serbia.
Administrative Divisions and Cities[]
Syria is divided into 13 governorates, which are sub-divided into 53 districts, which are further divided into sub-districts.

Administrative divisions of Syria, before Treaty of Aleppo.
| No. | Governorate | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Latakia | Latakia |
| 2 | Idlib | Idlib |
| 3 | Aleppo | Aleppo |
| 4 | Al Raqqah | Al Raqqah |
| 6 | Tartus | Tartus |
| 7 | Hama | Hama |
| 8 | Deir ez-Zor | Deir ez-Zor |
| 9 | Homs | Homs |
| 10 | Damascus | - |
| 11 | Rif Dimashq | - |
| 12 | Quneitra | Quneitra |
| 13 | Daraa | Daraa |
| 14 | Al-Suwayda | Al-Suwayda |
List of cities in Syria
| English Name | Arabic Name | Population | District | Governorate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aleppo | حلب | 2,132,100 | Mount Simeon District | Aleppo Governorate |
| Damascus | دمشق | 1,414,913 | Damascus (as a district) | Damascus Governorate |
| Daraa | درعا | 97,969 | Daraa District | Daraa Governorate |
| Deir ez-Zor | دير الزور | 211,857 | Deir ez-Zor District | Deir ez-Zor Governorate |
| Hama | حماة | 312,994 | Hama District | Hama Governorate |
| Homs | حمص | 652,609 | Homs District | Homs Governorate |
| Idlib | ادلب | 97,969 | Idlib District | Idlib Governorate |
| Latakia | اللاذقية | 383,786 | Latakia District | Latakia Governorate |
| Quneitra | القنيطرة | 153 | Quneitra District | Quneitra Governorate |
| Ar-Raqqah | الرقة | 220,488 | Al-Raqqah District | Ar-Raqqah Governorate |
| As-Suwayda | السويداء | 73,641 | As-Suwayda District | As-Suwayda Governorate |
| Tartus | طرطوس | 115,769 | Tartus District | Tartus Governorate |
| Abu Kamal | البوكمال | 42,510 | Abu Kamal District | Deir ez-Zor Governorate |
Economy[]
Coming Soon
Demographic[]
Coming Soon
Culture and Sports[]
Coming Soon




